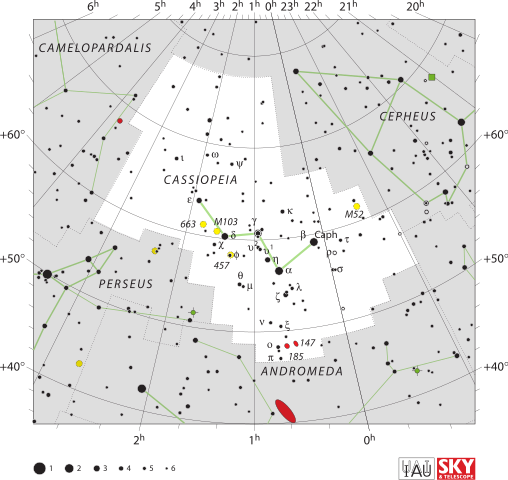
- How to find and observe NGC457 (TOTS#3) (eyesonthesky.com)
NGC 457 is an open cluster within our own Milky Way galaxy. It is over 7,900 light years from Earth, so the photons from it reaching your eye in a telescope left that cluster about the time copper was first being used in the Middle East. The estimated age is about 21 million years, making it one of the younger star clusters in our galaxy. Here is how to locate it.
- NGC 457 (Wikipedia)
NGC 457 (also designated Caldwell 13, and known as the Dragonfly Cluster, E.T. Cluster, Owl Cluster, Kachina Doll Cluster or Phi Cassiopeiae Cluster) is an open star cluster in the constellation Cassiopeia.