Be pacient therfore brethren vnto the commynge of the lorde. Beholde the husbande man wayteth for the precious frute of the erth and hath longe pacience ther vppon vntill he receave (the erly and the latter rayne.)
James 5:7 TYN
- Suiattle River (Wikipedia)
The Suiattle River (/suːˈætəl/ soo-AT-əl) is a river in the northern Cascade Mountains of western Washington, United States. It is a tributary of the Sauk River and by extension the Skagit River. Its source is located between Suiattle Glacier and Honeycomb Glacier on Glacier Peak, at an elevation of around 7,000 ft (2,100 m) above sea level. It descends through a 60-mile (97 km) course, lying mainly within the Mount Baker–Snoqualmie National Forest. It meets the Sauk northeast of Darrington, Washington, at an elevation of 400 ft (120 m). Snowmelt from Chocolate and Dusty Glacier gives the river silty water, with a suspended load over twice that of the upper Sauk or adjacent White Chuck.
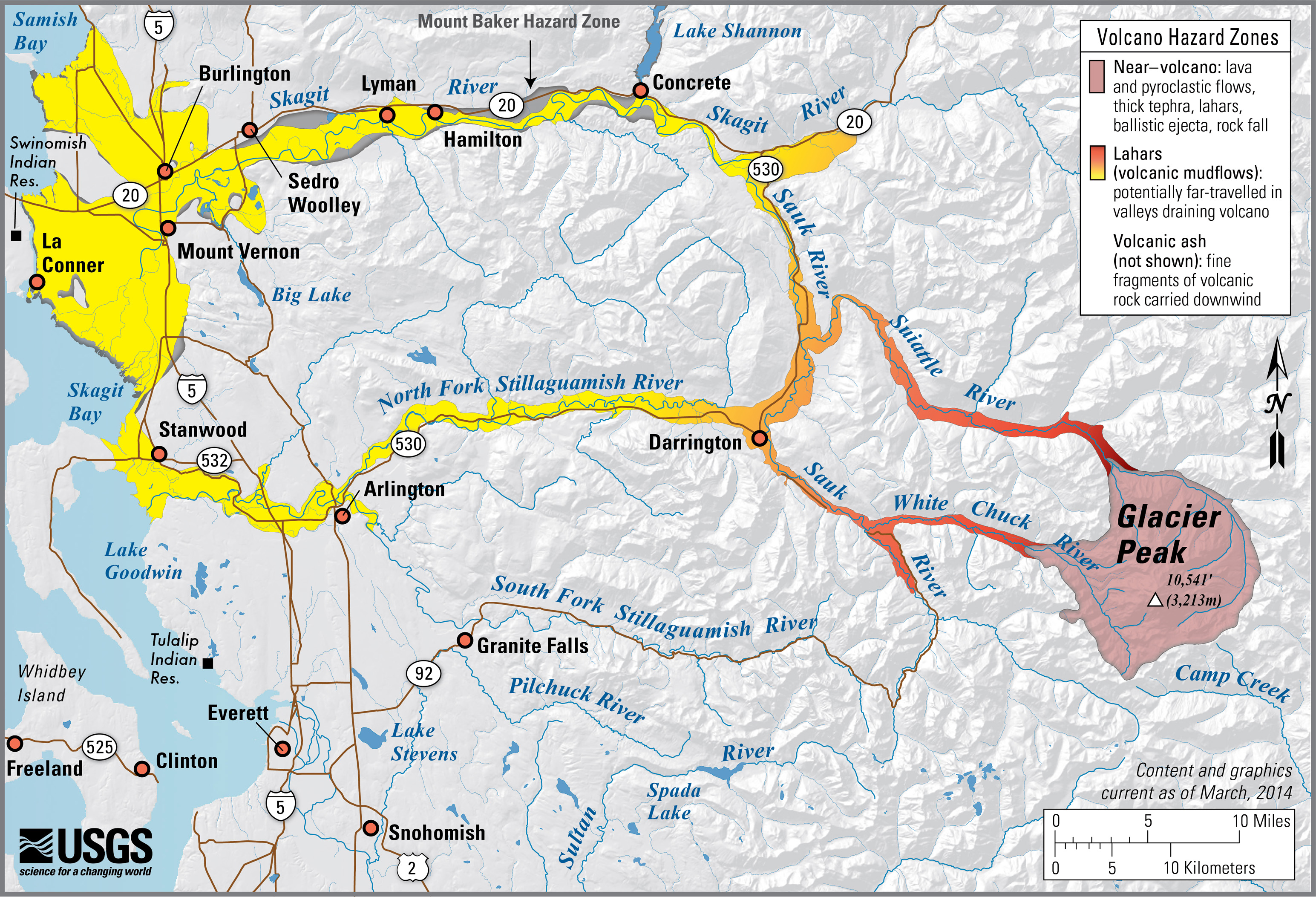 Glacier Peak, WA simplified hazards map (usgs.gov)
Glacier Peak, WA simplified hazards map (usgs.gov) Glacier Peak, WA simplified hazards map (usgs.gov)
Glacier Peak, WA simplified hazards map (usgs.gov)